what is appsa
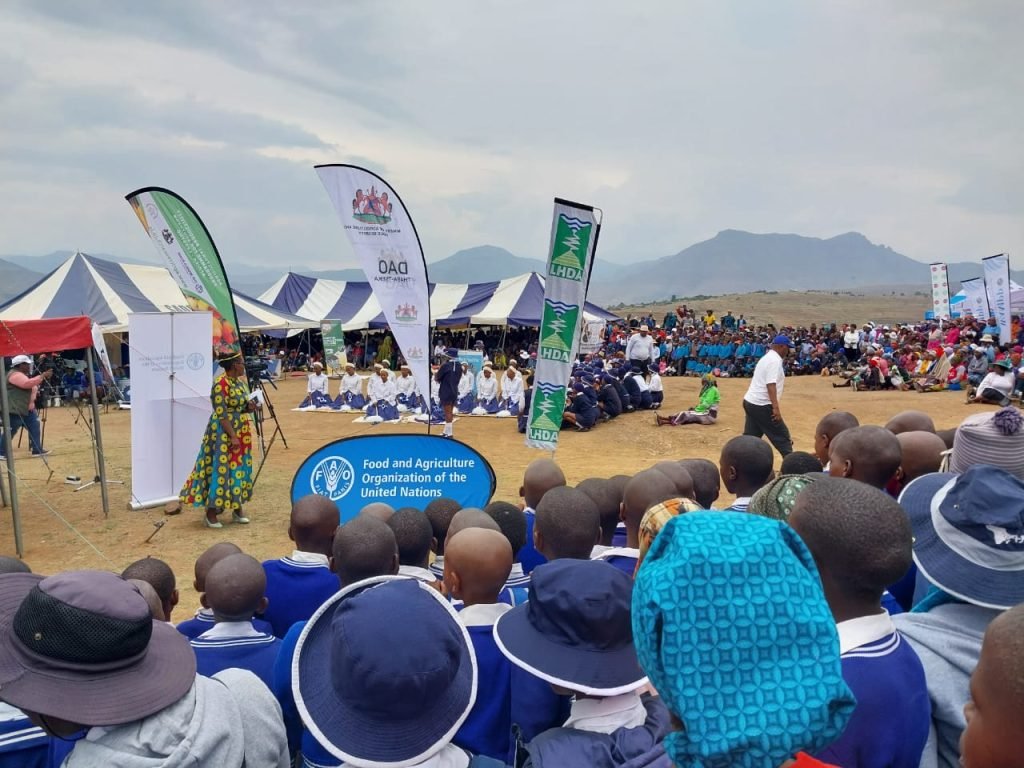
The Agricultural Productivity Program for Southern Africa (APPSA) Project is a regional project supported by separate World Bank (WB) – IDA1 credits to three countries in the region, namely Malawi, Mozambique and Zambia, and a World Bank – IDA grant for the Centre for Coordination of Agricultural Research and Development for Southern Africa (CCARDESA). The project was launched in all three countries and began activities in October/November 2013 and is expected to close by January 2020. APPSA seeks to promote regional collaboration and put in place mechanisms to encourage technology generation and dissemination across national borders of participating countries in the SADC region by:

- Supporting regional collaboration in agricultural research, technology dissemination, and training;
- Establishing Regional Centers of Leadership (RCoLs) on commodities of regional importance, and
- Facilitating increased sharing of agricultural information, knowledge, and technology among participating countries.
APPSA implementation is based on partnerships and collaboration among participating countries, promoting countries working together by undertaking joint technology generation, dissemination and training activities, by coordinating their respective activities in pursuit of common objectives; and by exchanging knowledge and technological outputs from their research programs. Research activities are undertaken through collaborative Research & Development (R&D) projects involving the participation of at least two countries and shall be focused on regional priorities.
overview
The Agricultural Productivity Programme for Southern Africa (APPSA) is a regional project supported by separate World Bank (WB) – IDA credits. The project originally started with three countries (Malawi, Mozambique and Zambia), and it has now extended to Lesotho and Angola. APPSA now has a World Bank – IDA grant component for the Centre for Coordination of Agricultural Research and Development for Southern Africa (CCARDESA). The first phase of three countries was launched in 2013 and officially closed in January 2020. Angola and Lesotho joined the APPSA Project in 2019 and are expected to implement the project until 2025.

project objectives
APPSA supports the objectives of the World Bank’s Africa Action Plan, which identifies regional integration as an important element for achieving higher economic growth and poverty reduction. Specifically APPSA aims to increase the availability of improved agricultural technologies in participating countries in the SADC region through:
Establishing Regional Centres of Leadership (RCoLs) on commodities of regional importance
Supporting regional collaboration in agricultural research, technology dissemination, and training
Facilitating increased sharing of agricultural information, knowledge, and technology among participating countries
project approach
Implementation of APPSA is based on partnerships and collaborations among SADC countries. Two or more countries are encouraged to partner and collaborate, Angola and Lesotho are collaborating to implement the current arrangement of APPSA while more countries are expected to join. Angola is focusing on cassava-based farming systems and will establish a Cassava Regional Centre of Leadership, while Lesotho is focusing on horticulture-based farming systems and will establish a Horticulture Regional Centre of Leadership. In the first phase, Malawi, Mozambique and Zambia established Regional Centres of Leadership in maize, rice and food-legumes based farming systems respectively which other countries in the region are expected to tap into. There Angola and Lesotho are also expected to work with the commodities that were adopted by the first three APPSA countries.
project development objectives (PDO)
The PDO is to increase the availability of improved agricultural technologies in participating countries in the SADC region.
pdo level indicators
1. Number of technologies that are being made available to farmers and other end-users
2. Percentage of Lead Farmers in targeted areas who are aware and adopt an improved technology promoted by the Project
3. Number of technologies generated or promoted by the Project in one participating country that are released in another participating country
4. Direct Project beneficiaries (number) of which female (percentage)
5. Farmers reached with agricultural assets or services
project components
While the components under APPSA Angola and Lesotho would remain largely the same as those under the original APPSA, a few modifications have been introduced based on lessons to date. The expanded APPSA which includes Angola and Lesotho is designed around four components:
1
Technology generation and dissemination
2
Strengthening regional centers of leadership
3
Contingency emergency response
4
Project management, monitoring and evaluation and Coordination
Some key modifications have been instituted for the two new APPSA countries as follows:
- The R&D sub-project cycle will be strengthened by including ‘concept incubation’ to ensure higher quality sub-projects are developed.
- Component 2 is being renamed and adjusted to allow institutional capacity building investments not just in Regional Centers of Leadership (RCoLs) but the larger enabling environment for technology dissemination and movement of technology within the region; and
- A new component on contingency emergency response has been added to redirect project resources for responding to an emergency or crisis, should the need arise.
APPSA project activities within Southern Africa aims to invest in interventions that will:
i
Enhance regional specialization in agricultural research
ii
Enhance collaboration in agriculture training and technology dissemination
iii
Facilitate increased transfer of agricultural technology, information, and knowledge across national boundaries of these countries
The main objective of the Lesotho RCoL is to develop plant materials of high economic value which will:
- exhibit desirable traits (in terms of yield; pest and disease resistance; drought tolerance and market value)
- and also promote technology transfer through strengthening of institutional linkages both locally and regionally
These activities will be coordinated from the campus of the Department of Agricultural Research (DAR) Main station in Maseru and other four Regional stations spread across the different agro-ecological zones of the country which includes:
There will also be activities carried out with partner stakeholders within the larger National Agricultural Research System (NARS) at the National university of Lesotho and Lesotho Agricultural College as local APPSA collaborating partners.
The APPSA Lesotho outputs will be as follows:
i
Crop Genetic Diversity increased.
ii
Horticulture breeding program established.
iii
Pest and disease management mechanisms enhanced.
iv
Postharvest technologies improved.
v
Irrigation and Mechanization technologies / innovations developed
vi
Production systems and management technologies developed.
vii
Dissemination and technology transfer techniques developed.
viii
Planting material systems strengthened.
ix
Research technologies exchange with other regional research institutions enhanced.
x
Farmer capacitated on horticulture-based farming system.
xi
Laboratories for research and community service improved.
xii
Legal framework setup to facilitate R&D
appsa consists of three components:

Technology Generation and Dissemination
Strengthening Regional Centers of Leadership

Coordination and Facilitation
The project with a total budget of US$ 20m (Annex 1) will support agricultural research, technology dissemination, and capacity building activities associated with RCoLs. Priority farming systems for each RCoL were identified on the basis of a regional priority-setting study that identified leading R&D priorities for the SADC region, as well as the priorities indicated by each country. To this effect Malawi, Mozambique and Zambia for the first phase of APPSA focused on maize, rice and food legumes farming systems respectively. Phase 2 of APPSA RCoLs elected horticulture-based farming system and cassava–based farming system for both Lesotho and Angola respectively.
1.2.1 Program Objectives, Indicators and Outcomes
The Lesotho APPSA log frame outlines the key features that lead to the project achieving its goal of increasing production and productivity of horticulture-based farming system. APPSA results reporting will be done according to the indicators and targets included in the logical framework. Following this a disaggregated baseline data need to be provided from the regional research stations targeted by the project. This data is important as it establishes the starting point from which results attributable to the APPSA will be measured during project implementation.
1.2.2 Project Beneficiaries
The primary beneficiaries of APPSA are farmers and other potential end users of the improved technology and knowledge generated and/or disseminated by the Project. APPSA will work with a subset of the primary beneficiaries; lead farmers who will contribute to setting R&D priorities and participate in on-farm trials, technology demonstrations, and training activities. APPSA will also benefit other stakeholders within the NARS: agricultural researchers; extension agents and advisory service providers; and seed producers and suppliers. These groups will benefit by participating in R&D projects and training activities, or by using technology and knowledge made available through the Project. At least 30 percent of all lead farmers and others targeted for participation in APPSA activities will be female, which is in line with World Bank requirements.
